
This paper analyzes the design requirements of a new generation airfoil from several aspects. Broadband stealth, long range, and high maneuver are required by future fighter aircrafts which are very likely to adopt the ultra-flat tailless aerodynamic layout. According to the requirement development of the next-generation fighters, the airfoil design has gradually developed from focusing only on single aerodynamic requirement to multi-objective and multi-disciplinary design. Based on the review of aerodynamic characteristics of fighters from the first to the fourth generation, this paper summarizes the design characteristics and development trend of airfoils for fighters. Innovation and breakthrough are absolutely necessary in the airfoil design of next-generation fighters. And the airfoil is the basic element of wings. Finally, the reliability of this method is verified by an airfoil design process based on the X47-B layout.Ībstract: Wing is the most important part to realize the aerodynamic performance of fighters. This multi-disciplinary collaborative global/local optimization method can quickly realize the airfoil design that meets the performance requirements of multi-section flying wing layouts, and can effectively improve the performance and design efficiency of designed airfoils. According to aerodynamic design requirements of flying wings, an efficient proxy model based on partitioned airfoils for global optimization design and a refined local optimization design method for three-dimensional layouts are established and integrated. Consequently, a global/local airfoil multidisciplinary design method is proposed. Since traditional airfoil design methods do not take the cross-flow effect into account, their applications in designing three-dimensional airfoil layouts cannot achieve desired performance. Aerodynamic design requirements for different spanwise partitions of flying wings are then put forward for the design of partitioned airfoils. Aerodynamic characteristics and design requirements of flying-wing layouts are firstly analyzed. With the strong need of developing future aircrafts and other aerodynamics-related equipments, a general trend of developing new-generation airfoils is to achieve better multidisciplinary performance when flying at wider speed ranges, larger airspace and multi-physics enviroments or intelligent morphing, which presents great challenges for numerical simulations, design optimization, and experimental validations.Ībstract: This paper proposes a new design method for aircrafts with flying-wing layouts. Future challenges as well as research directions are presented as the outcome of this review. This article focuses on reviewing the recent progress on airfoil research after a brief review of over 100 years’ history of airfoil research and development. In the 21 st century, high-fidelity numerical simulations, multi-objective multi-constraint optimization, flow instability analysis theory and transition prediction methods, and experimental testing techniques have been advanced progressively, which places a sound base for the development of new-generation airfoils. A large number of airfoil families, such as RAE, DVL, NACA, and TsAGI, either for general purpose or for particular types of aircrafts flying at different speed regimes, as well as airfoil families dedicated to helicopter rotors, propeller blades, and wing-turbine blades have been developed.


Since the invention of the first aircraft in the early 20th century, each breakthrough in airfoil research has dramatically promoted the upgrading of a better-performance aircraft.
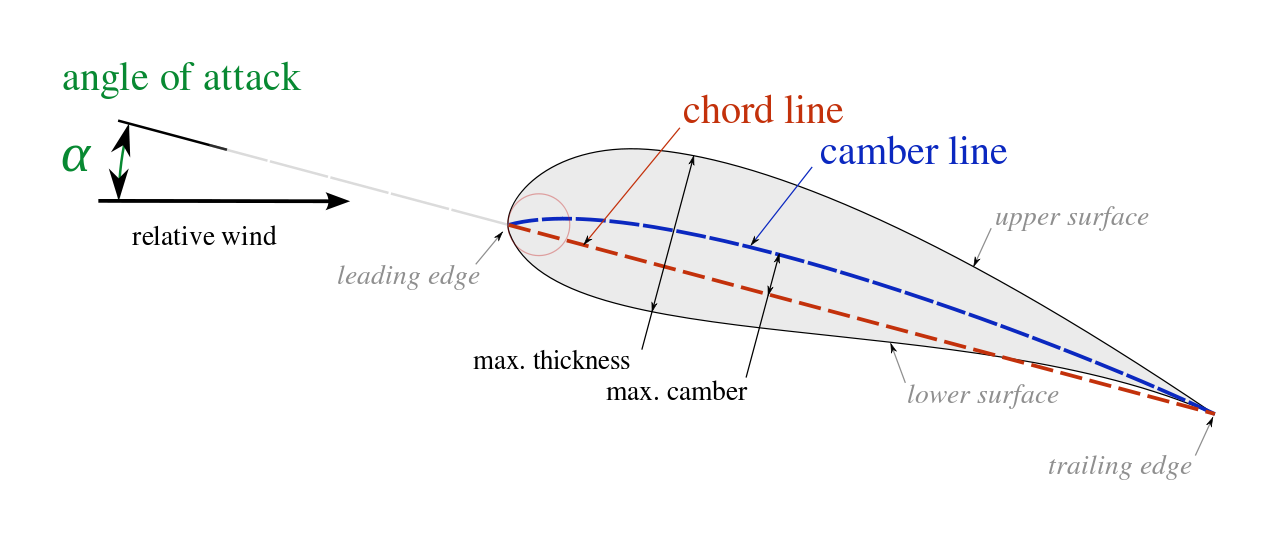

Abstract: Airfoils, which are the cross-section profiles of aircraft wings and tails, missile fins, helicopter rotor blades, and wind turbine propellers, play a particularly important role in determining the aerodynamic and overall performance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
